Getting Started with Gardening
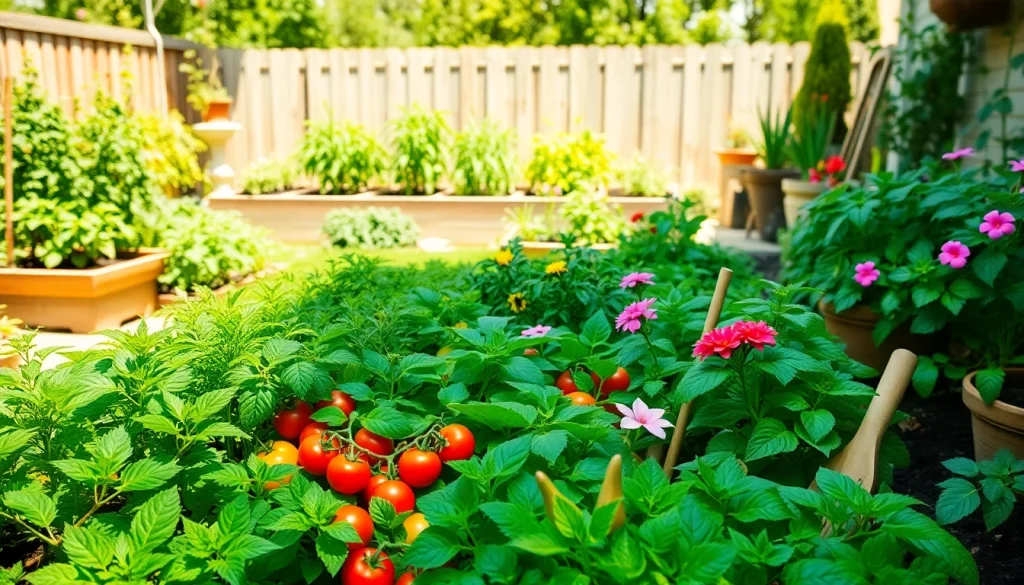
For many, Gardening is more than just a hobby; it’s a way to reconnect with nature and cultivate one’s self-sufficiency. The joy of nurturing plants, watching seeds sprout, and eventually enjoying the fruits of your labor is unparalleled. This guide will explore everything you need to know to kickstart your gardening journey, whether you want to cultivate a vibrant flower garden, grow fresh vegetables, or simply enjoy the tranquility that comes with tending to a garden.
Choosing the Right Location for Your Garden
The first step to successful Gardening is selecting the appropriate location. Factors such as sunlight, accessibility, water supply, and wind protection all play crucial roles.
Sunlight
Most plants require at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight daily. Observe your yard or garden area at various times during the day to determine the sunniest spots.
Accessibility
Ensure that the location is easily accessible for regular maintenance tasks like watering, weeding, and harvesting. Close proximity to your home makes it more likely you will engage with your garden.
Water Supply
Having a water source nearby is essential. Consider the placement of your garden relative to hoses, irrigation systems, or natural water sources.
Wind Protection
Strong winds can damage delicate plants. Establish barriers, such as hedges or fences, to protect your garden from harsh weather conditions.
Understanding Soil Types for Gardening Success
Healthy soil is the foundation of any successful garden. Understanding the types of soil and their properties can help you optimize growth conditions.
Types of Soil
There are three primary soil types: sand, silt, and clay. Each type has unique characteristics affecting water retention, aeration, and nutrient availability.
- Sand: Drains quickly but doesn’t hold nutrients well.
- Silt: Holds moisture and nutrients effectively, making it ideal for most plants.
- Clay: Retains water, can compact easily, and may need amendment to improve drainage.
Testing and Amending Your Soil
Conduct a soil test to determine pH levels and nutrient content. Based on the results, you may need to amend your soil with organic matter, compost, or fertilizers to create the ideal growing conditions.
Selecting the Best Plants for Your Environment
Choosing the right plants based on your local climate and conditions is vital for successful Gardening. Consider the following aspects:
Climate Zones
Familiarize yourself with your hardiness zone, which indicates the average minimum temperatures in your area, helping you choose plants that will thrive in your local climate.
Native Plants
Incorporating native plants can greatly enhance the resilience of your garden while reducing maintenance costs. Native plants are adapted to the local environment, requiring less water and fertilizer.
Season Considerations
Understand the growing season for the plants you wish to grow. Some plants may thrive in spring, while others may prefer the cooler conditions of fall.
Basic Gardening Techniques
With the right location and soil prepared, it’s time to consider the basic techniques that will form the bedrock of your Gardening endeavors.
How to Plant: Step-by-Step Guide
Planting techniques may vary based on plant types, but here’s a basic step-by-step guide to get you started:
- Prepare your planting area by tilling the soil and removing debris or weeds.
- Follow the planting instructions for the specific plant, including planting depth and spacing.
- Dig a hole that is about twice the width of the root ball and just deep enough to plant the root system without bending any roots excessively.
- Place the plant in the hole, fill it with soil, and pat down gently to eliminate air pockets.
- Water thoroughly to settle the soil around the root and promote initial growth.
Watering and Fertilizing: Best Practices
Watering and fertilizing are critical components that will influence plant health and productivity. Here are some best practices:
Watering Techniques
Water deeply but infrequently to encourage deep root development. A general guideline is to provide about 1 inch of water per week, including rainfall.
Fertilizing Wisely
Consider organic fertilizers such as compost, manure, and bone meal to enrich your soil. Always test the soil first to avoid over-fertilization, which can harm your plants.
Essential Tools for Gardening Enthusiasts
Having the right tools can make Gardening far easier and more enjoyable. Here’s a roundup of essential tools every gardener should have:
- Hand trowel: Ideal for planting and transplanting.
- Pruning shears: Necessary for maintaining plant shape and health.
- Garden hoe: Useful for weeding and cultivating soil.
- Watering can or hose: Essential for providing water to your plants.
- Garden rake: Helps level soil and gather debris.
Common Gardening Challenges
Every gardener faces challenges, but understanding them and knowing how to combat them can lead to success. Below, we discuss some common issues and potential solutions.
Identifying and Treating Plant Diseases
Plant diseases can drain the life from your garden. Identifying symptoms early is key to effective treatment.
Common Symptoms
Yellowing leaves, wilting, and abnormal growth patterns often indicate disease. Familiarizing yourself with common plant diseases can enable early detection.
Management Strategies
Use proper spacing for air circulation, avoid wetting the foliage while watering, and rotate crops annually to limit disease spread.
Dealing with Pests in Your Garden
Pests can wreak havoc on your plants. Knowing how to identify them and deploy effective strategies can make a significant difference.
Identifying Pests
Common pests include aphids, beetles, and caterpillars. Look for signs like holes in leaves or an unusual number of insects.
Prevention and Control
Encourage beneficial insects, use natural predators, and apply organic pesticides as a last resort to minimize the impact of harmful pests.
Overcoming Weather Issues and Climate Effects
Weather fluctuations can affect gardening. Understanding your local climate and being prepared can mitigate potential damage.
Hot Weather Strategies
During heatwaves, shade plants and apply mulch to retain moisture.
Cold Weather Approaches
Using row covers and planting cool-weather crops in late summer for early spring harvest can help manage colder temperatures.
Advanced Gardening Strategies
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you might want to explore advanced techniques to take your Gardening to the next level.
Companion Planting for Better Yields
Certain plant combinations can enhance growth and deter pests. Understanding companion planting can significantly benefit your garden.
- Tomatoes and Basil: Basil can enhance tomato growth and flavor.
- Carrots and Onions: Onions can repel pests that typically harm carrots.
- Beans and Corn: Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, benefitting corn.
Vertical Gardening: Maximizing Small Spaces
Vertical gardening allows effective space use, especially in urban areas where ground space is limited. Here are some methods:
Trellising
Use trellises to support growing plants like cucumbers and peas, allowing them to grow upwards instead of sprawling.
Container Gardening
Utilize pots, hanging baskets, and wall planters to create attractive and productive vertical gardens.
Tech Tips: Using Technology in Gardening
Modern technology can streamline gardening tasks and enhance productivity. Here are some tech tools to consider:
Gardening Apps
Apps can track growth, remind you of watering schedules, and provide information tailored to your local environment.
Automated Watering Systems
Implementing drip irrigation can optimize water use and ensure your plants receive consistent moisture.
Maintaining Your Garden Throughout the Year
Once established, continuous maintenance is vital for a flourishing garden. Here are strategies to keep your garden thriving from season to season.
Seasonal Planting and Care Calendar
Adhering to a seasonal calendar can ensure you’re planting and maintaining plants at the ideal times. Here’s a simplified guide:
- Spring: Time for sowing seeds, planting seedlings, and general garden preparation.
- Summer: Regular watering, weeding, and monitoring for pests are crucial during this growth phase.
- Fall: Time for harvesting, planting cover crops, and preparing beds for winter.
- Winter: Assess garden needs, plan for next year, and protect plants susceptible to cold.
Preparing Your Garden for Winter
Winter preparation is crucial; here’s how to safeguard your plants:
- Mulching: Applying mulch can protect plant roots from freezing and thawing.
- Covering tender plants: Use frost cloths or row covers to protect delicate varieties.
Harvesting: When and How to Reap Your Rewards
Harvesting at the right time ensures peak flavor and nutritional value:
- Timing: Harvest vegetables when they are ripe; this varies for each crop.
- Technique: Use clean, sharp tools to prevent damaging the plant and encourage future growth.