Understanding Warehousing: Definition and Basics
What is Warehousing?
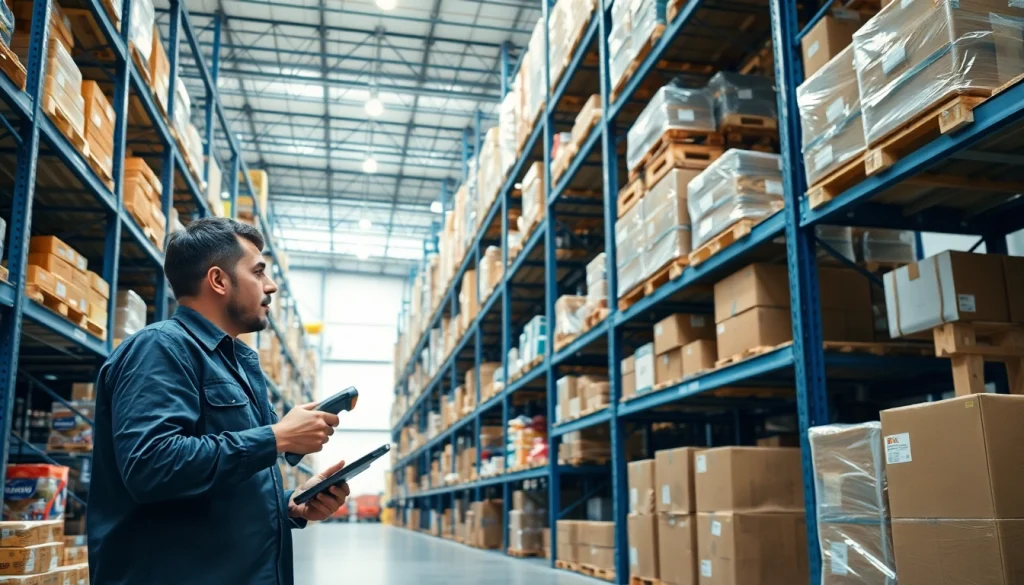
Warehousing refers to the strategic process of storing goods in well-organized facilities, ensuring products are available when needed. It serves as a crucial link in the supply chain, connecting manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers to consumers. This storage facility allows for the efficient management and allocation of products, including inventory management, ensuring that businesses can effectively meet customer demand.
A warehouse is more than just a large storage space. It serves various functions such as receiving, storing, and distributing products. warehousing is essential for managing supply flow and handling logistics, making it a backbone of modern commerce. A well-organized warehouse ensures that goods remain in optimal condition and are ready for transport when needed, thereby minimizing delays in distribution.
Essential Functions of Warehousing
The functions of warehousing can be categorized into several essential roles:
- Storage: This is the most apparent function, where goods are held until they are needed.
- Inventory Management: Keeping track of stock levels, understanding market demand, and adjusting orders accordingly.
- Order Fulfillment: Picking, packing, and preparing goods for delivery.
- Cross-Docking: Moving goods directly from incoming to outgoing transport, reducing handling times.
- Value-Added Services: These can include packaging, labeling, and assembling products to meet specific customer requirements.
Types of Warehousing Solutions
Understanding the different types of warehousing can help businesses select the right solution for their needs:
- Public Warehousing: Operated as an independent business offering storage space and services to multiple clients.
- Private Warehousing: Owned and operated by a single company to store its products, allowing for complete control and customization.
- Contract Warehousing: A combination of public and private options, where a company contracts a third party to manage its warehousing needs.
- Distribution Centers: Specialized warehouses designed specifically for quick distribution and logistics operations, reducing delivery times to retailers or consumers.
- Climate-Controlled Warehousing: Facilities that maintain specific temperature and humidity levels suitable for sensitive products like food and pharmaceuticals.
Importance of Warehousing in Supply Chain Management
Role of Warehousing in Logistics
Warehousing plays an integral role in logistics by acting as a buffer between supply and demand. In a world where instant gratification is often expected, warehousing enables companies to stockpile products close to their customers, thereby minimizing transit times. This strategic positioning allows businesses to respond rapidly to customer demands, effectively reducing lead times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Additionally, warehousing facilitates better inventory control, ensuring that products are organized, easily located, and readily accessible. This efficiency in logistics operations contributes to a more responsive supply chain, ultimately improving overall business performance.
Impact on Distribution Efficiency
The effectiveness of a warehouse significantly impacts distribution efficiency. A well-organized warehouse allows for smooth operations including receiving, storing, and dispatching goods. When efficient systems are in place, processes such as order picking and shipping can be streamlined, resulting in quicker turnaround times.
Moreover, the strategic use of technology, like warehouse management systems (WMS) and automation tools, can optimize operations further, ensuring that goods are tracked, stored, and dispatched with minimal errors. This optimization directly translates to cost savings, reduced waste, and improved service levels.
Case Studies of Successful Warehousing Operations
Examining successful warehousing operations offers valuable insights:
One notable case is the implementation of automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) by several leading logistics companies. These systems not only reduce labor costs but also enhance inventory accuracy and maximize storage space. AS/RS can efficiently manage thousands of SKUs, allowing for rapid access and efficient order fulfillment.
Another example includes company X, which leveraged cross-docking strategies to minimize handling and storage costs. By coordinating inbound and outbound logistics, this company successfully reduced inventory holding costs and delivery times, leading to higher customer satisfaction and significant cost savings.
Best Practices for Optimal Warehousing Operations
Implementing Organizational Strategies
Effective organizational strategies are foundational to successful warehousing operations. Businesses should consider these best practices:
- Layout Optimization: Design the warehouse layout to facilitate efficient movement of goods. This includes logical arrangements of storage racks, packing stations, and loading docks.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop clear SOPs for all warehouse functions to ensure consistency and efficiency in operations.
- Regular Training: Providing ongoing training ensures that staff are up-to-date with the latest warehousing techniques, safety protocols, and technology.
- Inventory Rotation: Implement FIFO (First In, First Out) or LIFO (Last In, First Out) strategies based on product type and shelf life to minimize obsolescence and waste.
Utilizing Technology in Warehousing
Technology is rapidly transforming warehousing operations. Here are some innovative applications:
- Warehouse Management Systems: A WMS streamlines operations by facilitating real-time inventory tracking and management, order fulfillment, and reporting.
- Automation: Automated systems, including robotic pickers and conveyor systems, reduce manual labor and increase efficiency by speeding up storage and retrieval processes.
- Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics can provide actionable insights for improving efficiency, predicting demand, and optimizing stock levels.
- Barcode and RFID Technology: Implementing barcode scanning or RFID systems enhances inventory accuracy and speeds up location and retrieval processes.
Safety Standards and Regulations in Warehousing
Maintaining a safe work environment in warehouses is paramount. Adhering to safety standards can reduce accidents and boosts overall efficiency. Key safety practices include:
- Regular Safety Training: Conduct comprehensive safety training and drills for all employees to maintain awareness and preparedness.
- Proper Equipment Use: Ensure that staff are trained to operate all equipment safely, including forklifts and pallet jacks.
- Clear Signage: Use clear signage throughout the warehouse to indicate safety protocols and emergency exits.
- Regular Inspections: Frequent inspections and audits can help identify and rectify potential hazards before they lead to accidents.
Challenges Faced in Modern Warehousing
Common Warehousing Issues
Despite advancements in technology and processes, many warehouses still face challenges, including:
- Labor Shortages: The logistics sector is frequently impacted by workforce shortages, especially for skilled positions.
- Inventory Management Challenges: Balancing stock levels while avoiding overstocking or stockouts remains a persistent issue.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global events can significantly impact supply chains, resulting in delays and increased costs.
- Rising Costs: Escalating operational and overhead costs challenge warehouse profitability.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions, such as:
- Flexible Workforce Strategies: Consider employing temporary labor during peak seasons or increase automation to offset labor shortages.
- Enhanced Forecasting: Utilize advanced analytics to better predict demand and adjust inventory levels dynamically.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Diversify suppliers to reduce reliance on a single source, thus mitigating risks associated with disruptions.
- Cost-Reduction Initiatives: Regularly review operational expenses and identify areas for cost savings, such as energy-efficient systems or optimized logistics routes.
Future Trends in Warehousing
The future of warehousing is shaped by several emerging trends:
- Increased Automation: The growing reliance on automation, from robots to AI-driven systems, will continue to transform warehousing efficiency and accuracy.
- Eco-Friendly Practices: Sustainable warehousing practices, including energy-efficient buildings and waste reduction, will become a priority as businesses strive for environmental responsibility.
- Integration of IoT: The Internet of Things (IoT) will further enhance inventory tracking and warehouse monitoring, providing real-time data for decision-making.
- Focus on Simplified Returns Management: As e-commerce grows, warehouses will need to streamline returns processes to enhance customer satisfaction and reduce handling times.
Measuring Performance in Warehousing
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Warehousing
To ensure warehouse operations are effective, businesses should track several key performance indicators (KPIs):
- Order Accuracy Rate: Measures the percentage of orders correctly fulfilled.
- Inventory Turnover Ratio: Indicates how frequently stock is sold and replaced over a specific period.
- Warehouse Capacity Utilization: Assesses how effectively space is utilized within the warehouse.
- Average Delivery Time: Tracks the time taken from order placement to delivery.
Improving Warehouse Efficiency
Enhancing warehouse efficiency can significantly boost productivity. Consider these strategies:
- Process Automation: Automating repetitive tasks can free up human resources for more complex operations.
- Lean Principles: Apply lean principles to reduce waste and create more efficient workflows.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review processes and seek feedback from staff to identify improvement opportunities.
Tools for Tracking and Analyzing Performance
Several tools can assist in tracking and analyzing warehouse performance:
- Warehouse Management Software: Invest in WMS solutions for real-time tracking and performance analytics.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Utilize data analytics tools that integrate with your WMS to provide insights into performance metrics.
- Mobile Technology: Employ mobile devices and applications to facilitate on-the-go data collection and analysis.